x Các doanh nghiệp, shop kinh doanh online muốn tối ưu hóa chuỗi cung ứng để giảm chi phí, nâng cao chất lượng sản phẩm và dịch vụ khách hàng nên cần tìm hiểu về Inbound Logistics?
x Bạn muốn biết Inbound Logistics đóng vai trò quan trọng ra sao với doanh nghiệp?
x Bạn phân biệt được Inbound Logistics với Outbound Logistics và quy trình hoạt động của Inbound Logistics ra sao?
Proship.vn chúng tôi sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ Inbound Logistics là gì, Inbound Logistics đóng vai trò quan trọng ra sao, quy trình hoạt động của Inbound Logistics diễn ra thế nào,…cùng với đó là thách thức và các nhân tố ảnh hưởng tới hoạt động Inbound Logistics.
Inbound logistics là gì?
Inbound Logistics là gì? Là logistics đầu vào hay nguồn cung ứng nguyên vật liệu là quá trình hoạt động kiểm soát nguồn nguyên liệu thô hoặc bán thành phẩm từ nhà sản xuất hoặc nhà cung ứng.
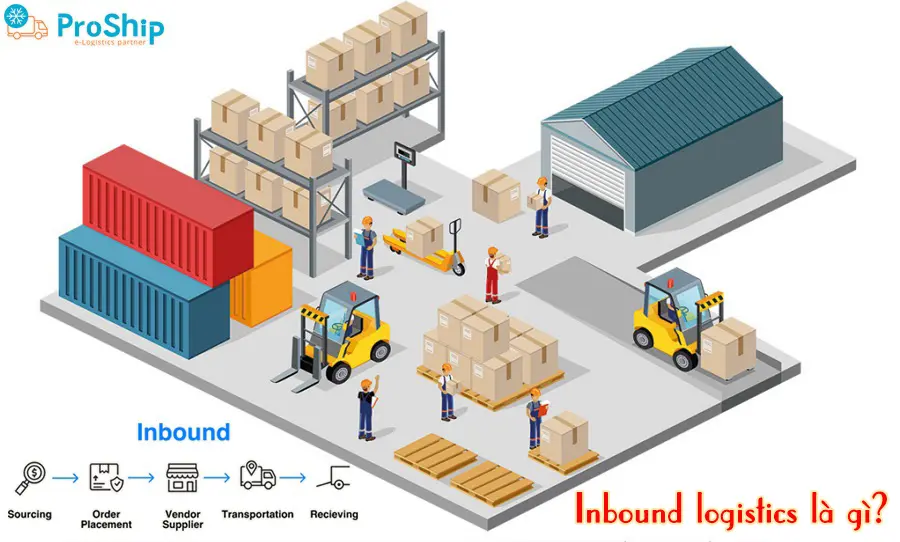
Inbound logistics như giai đoạn khởi đầu trong chuỗi cung ứng và là giai đoạn quyết định tình trạng hoạt động của các giai đoạn sau đó nên khá phức tạp và cần chỉn chu ngay từ đầu.
Tất tần tật kiến thức cần biết về Inbound Logistics
Inbound Logistics là gì đã được giải đáp ở trên. Tiếp theo là những kiến thức khác cần biết về logistics đầu vào:
Tầm quan trọng của Inbound logistics
Logistics đầu vào mang lại nhiều lợi ích quan trọng như:
- Tiết kiệm chi phí đầu vào:
Quản lý tốt Inbound logistics giúp shop thương lượng giá tốt với nhà cung cấp, tối ưu chi phí vận chuyển, lưu kho và giảm chi phí nguyên vật liệu đầu vào.
- Tăng tính linh hoạt và khả năng đáp ứng:
Logistics đầu vào hiệu quả giúp shop chủ động trong cung ứng nguyên vật liệu, đáp ứng nhanh nhu cầu sản xuất và biến động của thị trường.
- Nâng cao chất lượng sản phẩm:
Logistics đầu vào đảm bảo nguồn cung ứng nguyên vật liệu chất lượng, đáp ứng yêu cầu sản xuất và tạo ra sản phẩm chất lượng cao.
- Tối ưu không gian sử dụng kho:
Lập kế hoạch và quản lý Inbound logistics khoa học giúp chủ shop sắp xếp, lưu trữ nguyên vật liệu hợp lý, tối ưu không gian kho bãi và giảm lãng phí.
Các nhân tố ảnh hưởng tới Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics chịu tác động bởi nhiều yếu tố như:
- Đặc tính nguyên vật liệu:
Các thuộc tính cốt lõi của nguyên vật liệu như kích thước, khối lượng, tính dễ hư hỏng, tần suất sử dụng, giá trị sẽ quyết định phương thức vận chuyển, bảo quản, tần suất đặt hàng.
- Điều kiện cơ sở hạ tầng, dịch vụ logistics:
Sự phát triển cơ sở hạ tầng giao thông, kho bãi và chất lượng của các nhà cung cấp dịch vụ logistics bên ngoài sẽ tạo thuận lợi hoặc cản trở cho inbound logistics.
- Mối quan hệ với nhà cung cấp:
Sự tin cậy, ổn định và khả năng đáp ứng của nhà cung cấp tác động đến chất lượng, giá cả và thời gian cung ứng nguyên vật liệu.
- Năng lực đội ngũ Inbound logistics:
Trình độ chuyên môn, kỹ năng quản trị, tư duy sáng tạo và khả năng xử lý vấn đề của nhân sự làm inbound logistics ảnh hưởng lớn đến kết quả hoạt động này.
- Trình độ ứng dụng công nghệ:
Việc trang bị các giải pháp công nghệ tiên tiến trong quản lý đặt hàng, theo dõi hàng tồn kho, điều phối vận chuyển giúp tăng tính chính xác, nhanh chóng và hiệu quả của Inbound logistics.
Thách thức, cách tối ưu hoạt động Inbound logistics
Những thách thức gặp phải của Logistics đầu vào:
- Nhà cung cấp gặp vấn đề không thể cung cấp nguyên vật liệu:
Cần đa dạng hóa nguồn cung, ký kết hợp đồng, dự báo nhu cầu chính xác và theo dõi sát sao hoạt động của Nhà cung cấp để giảm rủi ro gián đoạn cung ứng.
- Rủi ro vận chuyển chậm trễ:
Để hàng hóa được vận chuyển đúng hạn và an toàn, nên chọn đối tác vận chuyển uy tín, theo dõi sát sao lộ trình vận chuyển, chọn phương thức vận chuyển phù hợp.
- Hoạt động quản lý thiếu sự chính xác, dễ sai sót:
Các shop nên ứng dụng phần mềm quản lý, chuẩn hóa quy trình và kiểm kê định kỳ. Qua đó hỗ trợ nâng cao hiệu quả quản lý, giảm sai sót, tăng tính chuẩn xác trong Inbound logistics.
- Khó khăn với hệ thống kho bãi:
Nếu các shop vừa và nhỏ chưa có khả năng sở hữu kho bãi riêng, shop nên sử dụng dịch vụ kho bãi bên thứ ba như Dịch vụ Cho thuê kho Ngoại quan (Bonded Warehouse) giá rẻ của Proship để đảm bảo điều kiện bảo quản hàng được tốt nhất.
- Hàng bị trả lại:
Các shop kinh doanh cần kiểm soát chất lượng đầu vào, đóng gói cẩn thận, cung cấp thông tin sản phẩm chính xác, xây dựng chính sách đổi trả hợp lý và phân tích nguyên nhân trả hàng.
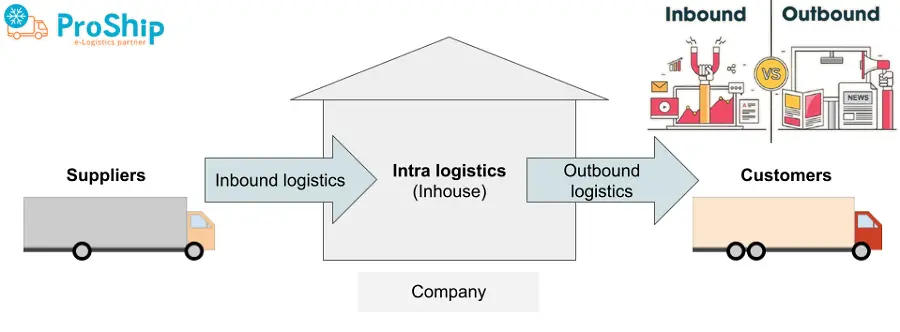
Sự khác nhau giữa Inbound Logistics và Outbound Logistics
Sự khác nhau giữa Outbound Logistics với Inbound Logistics là gì? Đó là:
| Tiêu chí | Logistics đầu vào
(Inbound Logistics) |
Logistics đầu ra
(Outbound Logistics) |
|---|---|---|
| Quy trình thực hiện | Là quá trình tìm kiếm, thu mua, vận chuyển và giao nguyên vật liệu, dụng cụ,…đến nhà kho, nhà máy, cơ sở sản xuất hoặc cửa hàng bán lẻ. | Là quá trình lập kế hoạch, thực hiện hoạt động phân phối hàng hóa đến người tiêu dùng cuối cùng. |
| Mối quan hệ | Giữa nhà cung cấp nguyên vật liệu với nhà máy, công ty sản xuất. | Giữa công ty sản xuất với người tiêu dùng cuối cùng. |
| Tối ưu | Just in time | Chi phí |
| Hoạt động chủ yếu | Thu mua, lưu trữ và phân phối nguyên vật liệu đến nơi sản xuất. | Đóng gói và phân phối hàng hóa đến người tiêu dùng cuối cùng. |
Quy trình hoạt động Inbound Logistics ra sao?
Quy trình hoạt động của Inbound Logistics diễn ra như sau:
Bước 1: Tìm kiếm đơn vị cung ứng nguyên vật liệu
Điều tra và báo cáo thông tin nhà cung ứng tiềm năng. Tiến hành nhận báo giá, thoả thuận, phân loại và quản lý danh sách nhà cung ứng.
Bước 2: Mua hàng
Khi chọn được đơn vị phù hợp, doanh nghiệp sẽ đặt mua nguyên vật liệu thiết yếu. Đồng thời thông báo thời gian mua hàng để quá trình sản xuất không ảnh hưởng và diễn ra liên tục.
Bước 3: Vận tải hàng hóa
Doanh nghiệp xem xét chọn hình thức vận tải, vận tốc giao hàng và ký Hợp đồng giá cả cùng lộ trình với bên vận chuyển.
Bước 4: Tiếp nhận và xử lý hàng
Nhận hàng tại địa điểm thỏa thuận, bốc dỡ hàng xuống bãi và kiểm tra số lượng có đúng như đơn hàng không.

Bước 5: Nhập kho và lưu trữ
Vận chuyển nguyên vật liệu về lưu kho hay bàn giao cho bên nhận hàng.
Bước 6: Quản lý tồn kho
Quản lý hàng hóa/nguyên liệu trước khi giao cho khách hay phục vụ sản xuất. Hàng hóa phải đặt đúng vị trí và bảo quản trong điều kiện theo quy ước chung.
Bước 7: Phân phối hàng
Nguyên vật liệu từ kho được phân phối đến các bộ phận sản xuất hoặc các điểm bán lẻ theo nhu cầu. Việc phân phối cần thực hiện kịp thời, đúng số lượng, địa điểm để hoạt động sản xuất kinh doanh được liên tục.
Bước 8: Thực hiện Logistics ngược
Logistics ngược (Reverse logistics) là quản lý quy trình hàng hóa từ người tiêu dùng về shop. Trong Inbound logistics, logistics ngược gồm việc xử lý hàng bị trả lại do lỗi, thu hồi bao bì, vỏ hộp để tái sử dụng,…
Inbound Logistics là gì và tất tần tật kiến thức về logistics đầu vào đã được chuyển tải bởi Proship. Các bên tham gia trong chuỗi cung ứng có thể áp dụng mô hình logistics đầu vào sao cho tối ưu và hiệu quả. Chúng tôi hiện là đơn vị Cho thuê kho ngoại quan Bonded Warehouse giá rẻ, Dịch vụ vận chuyển container đường biển, đường sắt, đường bộ,…liên hệ ngay 0909 344 247 để được tư vấn và báo giá tốt nhất.

