x Các doanh nghiệp, chủ hàng đang có lô hàng hóa có mẫu mã, tiêu chuẩn và chất lượng cụ thể cần thuê gia công làm theo đúng nguyên mẫu sản phẩm quy định?
x Bạn muốn tìm hiểu chi tiết về nội dung, quy định và cần cập nhật mới mẫu hợp đồng gia công hàng hóa, sản phẩm,…?
x Bạn muốn biết quyền và nghĩa vụ của bên đặt gia công với bên nhận gia công được quy định thế nào trong các hợp đồng gia công hiện nay?
Proship.vn chúng tôi sẽ giúp bạn hiểu được hợp đồng gia công là gì, hợp đồng gia công quy định những gì, bên đặt gia công và bên nhận gia công có quyền lợi và nghĩa vụ liên quan thế nào trong hợp đồng này. Đồng thời, qua đây bạn cũng biết được nếu đơn phương chấm dứt hợp đồng sẽ bị xử lý thế nào.
XEM THÊM: Nhận vận chuyển Container giá tốt
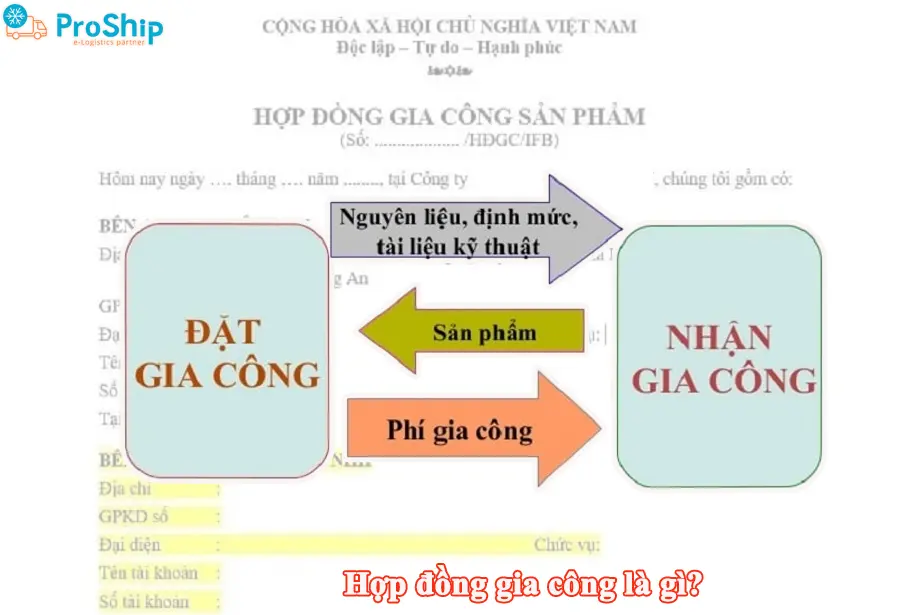
Hợp đồng gia công là gì?
Muốn hiểu một cách chính xác hợp đồng gia công là gì, bạn cần tham khảo Điều 524 Luật Dân sự 2015. Trích dẫn cụ thể:
“Hợp đồng gia công là sự thỏa thuận giữa các bên, theo đó bên nhận gia công thực hiện công việc để tạo ra sản phẩm theo yêu cầu của bên đặt gia công, bên đặt gia công nhận sản phẩm và trả tiền công.”
Mẫu hợp đồng gia công hàng hóa 2024
Proship cập nhật mẫu hợp đồng gia công cơ bản mới nhất 2024:
CỘNG HÒA XÃ HỘI CHỦ NGHĨA VIỆT NAM
Độc lập – Tự do – Hạnh phúc
——————-
HỢP ĐỒNG GIA CÔNG
Số: … /2018/HĐGC/
Hôm nay, ngày …………. tháng …………. năm …………….., Tại …………………
Chúng tôi gồm có:
Bên A: (Bên đặt hàng) …………………………………………………………………..
Địa chỉ: ……
Điện thoại: ………
Fax: ………
Mã số thuế: ………
Tài khoản số: …………………
Do ông (bà): ………………………
Chức vụ: ………………………… làm đại diện.
Bên B: (Bên sản xuất gia công)
Địa chỉ: ………
Điện thoại: ………
Fax: …………
Mã số thuế: ………
Tài khoản số: ……………………
Do ông (bà): ………………………
Chức vụ: ………………………….. làm đại diện.
Hai bên thống nhất thỏa thuận với nội dung hợp đồng như sau:
ĐIỀU 1: ĐỐI TƯỢNG CỦA HỢP ĐỒNG
1.1. Tên sản phẩm hàng hóa cần sản xuất:
1.2. Quy cách phẩm chất:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
ĐIỀU 2: NGUYÊN LIỆU CHÍNH VÀ PHỤ
2.1. Bên A có trách nhiệm cung ứng nguyên vật liệu chính gốm:
a) Tên từng loại ……… Số lượng ……….. Chất lượng ………………….
b) Thời gian giao ……………… Tại địa điểm: ……………………………..
c) Trách nhiệm bảo quản: Bên B chịu mọi trách nhiệm về số lượng, chất lượng các nguyên liệu do bên A cung ứng và phải sử dụng đúng loại nguyên liệu đã giao vào sản xuất sản phẩm.
2.2. Bên B có trách nhiệm cung ứng các phụ liệu để sản xuất:
a) Tên từng loại …………………… Số lượng …………….. Đơn giá (hoặc Quy định chất lượng theo hàm lượng, theo tiêu chuẩn) …………………………………………………….
b) Bên A cung ứng tiền trước để mua phụ liệu trên. Tổng chi phí là: ……………………………
ĐIỀU 3: QUYỀN VÀ NGHĨA VỤ CỦA BÊN A
3.1. Bên A có các nghĩa vụ sau đây:
a) Cung cấp nguyên vật liệu theo đúng số lượng, chất lượng, thời hạn và địa điểm cho bên B, trừ trường hợp có thoả thuận khác; cung cấp các giấy tờ cần thiết liên quan đến việc gia công;
b) Chỉ dẫn cho bên B thực hiện hợp đồng;
c) Chịu trách nhiệm đối với tính hợp pháp về quyền sở hữu trí tuệ của hàng hoá gia công, nguyên liệu, vật liệu, máy móc, thiết bị dùng để gia công chuyển cho bên B.
d) Trả tiền công theo đúng thỏa thuận.
3.2. Bên B có các quyền sau đây:
a) Nhận lại toàn bộ sản phẩm gia công, máy móc, thiết bị cho thuê hoặc cho mượn, nguyên, phụ liệu, vật tư, phế liệu, vật tư dư thừa, phế phẩm, phế liệu theo đúng số lượng, chất lượng, phương thức, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thoả thuận;
b) Cử người đại diện để kiểm tra, giám sát việc gia công tại nơi nhận gia công, cử chuyên gia để hướng dẫn kỹ thuật sản xuất và kiểm tra chất lượng sản phẩm gia công theo thoả thuận trong hợp đồng gia công.
c) Bán, tiêu hủy, tặng biếu tại chỗ sản phẩm gia công, máy móc, thiết bị cho thuê hoặc cho mượn, nguyên liệu, phụ liệu, vật tư dư thừa, phế phẩm, phế liệu theo thỏa thuận và phù hợp với quy định của pháp luật.
d) Đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng và yêu cầu bồi thường thiệt hại khi bên B vi phạm nghiêm trọng hợp đồng;
e) Trong trường hợp sản phẩm không bảo đảm chất lượng mà bên A đồng ý nhận sản phẩm và yêu cầu sửa chữa nhưng bên B không thể sửa chữa được trong thời hạn đã thỏa thuận thì bên A có quyền hủy bỏ hợp đồng và yêu cầu bồi thường thiệt hại.
ĐIỀU 4: QUYỀN VÀ NGHĨA VỤ CỦA BÊN B
4.1. Bên B có các nghĩa vụ sau đây:
a) Bảo quản nguyên vật liệu do bên A cung cấp;
b) Cung ứng một phần hoặc toàn bộ nguyên liệu, vật liệu để gia công theo thỏa thuận với bên A về số lượng, chất lượng, tiêu chuẩn kỹ thuật và giá.
c) Báo cho bên A biết để đổi nguyên vật liệu khác, nếu nguyên vật liệu không bảo đảm chất lượng; từ chối thực hiện gia công, nếu việc sử dụng nguyên vật liệu có thể tạo ra sản phẩm nguy hại cho xã hội; trường hợp không báo hoặc không từ chối thì phải chịu trách nhiệm về sản phẩm tạo ra;
d) Giao sản phẩm cho bên A đúng số lượng, chất lượng, phương thức, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thoả thuận;
e) Giữ bí mật các thông tin về quy trình gia công và sản phẩm tạo ra;
f) Chịu trách nhiệm về chất lượng sản phẩm, trừ trường hợp sản phẩm không bảo đảm chất lượng do nguyên vật liệu mà bên A cung cấp hoặc do sự chỉ dẫn không hợp lý của bên A.
g) Hoàn trả nguyên vật liệu còn lại cho bên A sau khi hoàn thành hợp đồng.
h) Chịu trách nhiệm về tính hợp pháp của hoạt động gia công hàng hóa trong trường hợp hàng hoá gia công thuộc diện cấm kinh doanh, cấm xuất khẩu, cấm nhập khẩu.
4.2. Bên B có các quyền sau đây:
a) Yêu cầu bên A giao nguyên vật liệu đúng chất lượng, số lượng, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thoả thuận;
b) Từ chối sự chỉ dẫn không hợp lý của bên A, nếu thấy chỉ dẫn đó có thể làm giảm chất lượng sản phẩm, nhưng phải báo ngay cho bên A;
c) Yêu cầu bên A trả đủ tiền công theo đúng thời hạn và phương thức đã thoả thuận.
ĐIỀU 5: THỜI GIAN SẢN XUẤT VÀ GIAO SẢN PHẨM
5.1. Bên B bắt đầu sản xuất từ ngày: …………………………
Trong quá trình sản xuất bên A có quyền kiểm tra và yêu cầu bên B sản xuất theo đúng mẫu sản phẩm đã thỏa thuận bắt đầu từ ngày đưa nguyên liệu vào sản xuất (nếu cần).
Thời gian giao nhận sản phẩm: ………………………………..
5.2. Nếu giao theo đợt thì:
a) Đợt 1: Ngày …………… địa điểm ………………………………………………………………..
b) Đợt 2: Ngày …………… địa điểm ………………………………………………………………..
c) Đợt 3: Ngày …………… địa điểm ………………………………………………………………..
Nếu bên A không nhận đúng thời gian sẽ bị phạt lưu kho là ………………
Nếu bên B không giao hàng đúng thời gian địa điểm sẽ phải bồi thường các chi phí ……………

ĐIỀU 6: CÁC ĐIỀU KHOẢN BẢO ĐẢM HỢP ĐỒNG (Nếu có)
ĐIỀU 7: THANH TOÁN
Thỏa thuận thanh toán toàn bộ hay từng đợt sau khi nhận hàng.
Thanh toán bằng tiền mặt hay chuyển khoản ……………………………
ĐIỀU 8: TRÁCH NHIỆM DO VI PHẠM HỢP ĐỒNG
7.1. Vi phạm về chất lượng: (làm lại, giảm giá, sửa chữa, bồi thường nguyên vật liệu…).
7.2. Vi phạm số lượng: Nguyên vật liệu hư hỏng phải bồi thường nguyên vật liệu theo giá hiện thời. ………………………………………………………
7.3. Ký hợp đồng mà không thực hiện: Bị phạt tới ……… % giá trị hợp đồng.
7.4. Vi phạm nghĩa vụ thanh toán: Bồi thường theo tỷ lệ lãi suất lãi suất ngân hàng.
ĐIỀU 9: THỦ TỤC GIẢI QUYẾT TRANH CHẤP HỢP ĐỒNG
8.1. Hai bên cần phải chủ động thông báo cho nhau biết tiến độ thực hiện hợp đồng, nếu có vấn đề bất lợi phát sinh các bên kịp thời báo cho nhau biết và chủ động bàn bạc giải quyết trên cơ sở thương lượng đảm bảo hai bên cùng có lợi (có lập biên bản).
8.2. Trường hợp có vấn đề tranh chấp không tự thương lượng được thì mới khiếu nại ra Tòa án.
ĐIỀU 10: CÁC THỎA THUẬN KHÁC (Nếu có)
ĐIỀU 11: HIỆU LỰC CỦA HỢP ĐỒNG
Hợp đồng này có hiệu lực từ ngày ……………………………. đến ngày …………………
Hai bên sẽ tổ chức họp và lập biên bản thanh lý hợp đồng sau đó ……… ngày. Bên A có trách nhiệm tổ chức vào thời gian, địa điểm thích hợp.
Hợp đồng được lập thành ………. (………..) bản, mỗi bên giữ một bản và có giá trị như nhau.
| ĐẠI DIỆN BÊN A | ĐẠI DIỆN BÊN B |
| Chức vụ (Ký tên, đóng dấu) |
Chức vụ (Ký tên, đóng dấu) |
ĐỌC THÊM: Vận chuyển Container lạnh giá tốt
Quy định về quyền, nghĩa vụ các bên trong hợp đồng gia công
Bạn cần nắm rõ một số quyền lợi và nghĩa vụ cơ bản của từng bên trong hợp đồng gia công là gì:
Với bên đặt gia công
Nghĩa vụ và quyền lợi của bên đặt gia công được quy định tương đối chi tiết tại Điều 544-545 Bộ Luật Dân sự 2015.
Các nghĩa vụ liên quan
, theo Điều 544, Nghĩa vụ của bên đặt gia công:
- Cung cấp nguyên vật liệu theo đúng số lượng, chất lượng, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thỏa thuận cho bên nhận gia công; cung cấp giấy tờ cần thiết liên quan đến việc gia công;
- Chỉ dẫn cho bên nhận gia công thực hiện hợp đồng;
- Trả tiền công theo đúng thỏa thuận.
Các quyền lợi liên quan
Quyền của bên đặt gia công, theo Điều 545:
- Nhận sản phẩm gia công theo đúng số lượng, chất lượng, phương thức, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thỏa thuận;
- Đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng và yêu cầu bồi thường thiệt hại khi bên nhận gia công vi phạm nghiêm trọng hợp đồng;
- Trường hợp sản phẩm không đảm bảo chất lượng mà bên đặt gia công đồng ý nhận sản phẩm và yêu cầu sửa chữa nhưng bên nhận gia công không thể sửa chữa được trong thời hạn thỏa thuận thì bên đặt gia công có quyền hủy bỏ hợp đồng và yêu cầu bồi thường thiệt hại.

Với bên nhận gia công
Theo Điều 546-547 trong cùng Bộ Luật Dân sự 2015, nghĩa vụ và quyền lợi của bên nhận gia công được quy định cụ thể như sau:
Các nghĩa vụ liên quan
Nghĩa vụ của bên nhận gia công, theo Điều 546:
- Bảo quản nguyên vật liệu do bên đặt gia công cung cấp;
- Báo cho bên đặt gia công biết để đổi nguyên vật liệu khác, nếu nguyên vật liệu không đảm bảo chất lượng; từ chối thực hiện gia công, nếu biết hoặc phải biết việc sử dụng nguyên vật liệu có thể tạo ra sản phẩm nguy hại cho xã hội;
- Giao sản phẩm cho bên đặt gia công đúng số lượng, chất lượng, phương thức, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thỏa thuận;
- Giữ bí mật thông tin về quy trình gia công và sản phẩm tạo ra;
- Chịu trách nhiệm về chất lượng sản phẩm, trừ trường hợp sản phẩm không đảm bảo chất lượng do nguyên vật liệu mà bên đặt gia công cung cấp hoặc do sự chỉ dẫn không hợp lý của bên đặt gia công;
- Hoàn trả nguyên vật liệu còn lại cho bên đặt gia công sau khi hoàn thành hợp đồng.
Các quyền lợi liên quan
Quyền của bên nhận gia công, theo Điều 547:
- Yêu cầu bên đặt gia công giao nguyên vật liệu đúng chất lượng, số lượng, thời hạn và địa điểm đã thỏa thuận;
- Từ chối sự chỉ dẫn không hợp lý của bên đặt gia công trong quá trình thực hiện hợp đồng, nếu thấy chỉ dẫn đó có thể làm giảm chất lượng sản phẩm, nhưng phải báo ngay cho bên đặt gia công;
- Yêu cầu bên đặt gia công trả đủ tiền công theo đúng thời hạn và phương thức đã thỏa thuận.
Quy định về việc đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng gia công
Theo quy định tại Điều 551 Bộ luật Dân sự 2015 như sau:
“Điều 551. Đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng gia công
1. Mỗi bên đều có quyền đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng gia công, nếu việc tiếp tục thực hiện hợp đồng không mang lại lợi ích cho mình, trừ trường hợp có thỏa thuận khác hoặc pháp luật có quy định khác, nhưng phải báo cho bên kia biết trước một thời gian hợp lý.
2. Bên đặt gia công đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng thì phải trả tiền công tương ứng với công việc đã làm, trừ trường hợp có thỏa thuận khác. Bên nhận gia công đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng thì không được trả tiền công, trừ trường hợp có thỏa thuận khác.3. Bên đơn phương chấm dứt thực hiện hợp đồng mà gây thiệt hại cho bên kia thì phải bồi thường”.
Hợp đồng gia công là gì, nội dung, mẫu hợp đồng cùng những quy định liên quan đã được cập nhật và chia sẻ bởi Proship Logistics. Quý doanh nghiệp có nhu cầu tìm hiểu về hợp đồng gia công may mặc, hợp đồng gia công phần mềm, hợp đồng gia công cơ khí hay nguyên liệu,…có thể tham khảo bài viết này và mọi thắc mắc, vui lòng liên hệ 0909 344 247 để được giải đáp.
