x Bên bán, bên mua,…trong hoạt động Thương mại quốc tế cần tìm hiểu về các điều kiện quan trọng trong Incoterm 2010 là gì?
x Bạn thắc mắc về vai trò và tầm quan trọng của Incoterm 2010 trong hoạt động Thương mại quốc tế ra sao?
x Bạn muốn tìm hiểu rõ khái niệm Incoterm 2010 nghĩa là gì?
Cùng Proship.vn chúng tôi tìm hiểu xem Incoterm 2010 có bao nhiêu điều kiện và Incoterm bản 2010 đóng vai trò quan trọng ra sao, mỗi điều kiện kèm theo những quy định gì,…ngay sau đây nhằm giải đáp nhanh mọi thắc mắc đặt ra ở trên.
Khái niệm Incoterms, Incoterms 2010 là gì?
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) là bộ quy tắc quốc tế do phòng Thương mại quốc tế (International Chamber of Commerce – ICC) phát hành để nêu ra các điều khoản thương mại quốc tế thông qua việc xác định trách nhiệm và nghĩa vụ của người bán, người mua trong các Hợp đồng mua bán hàng hóa quốc tế.
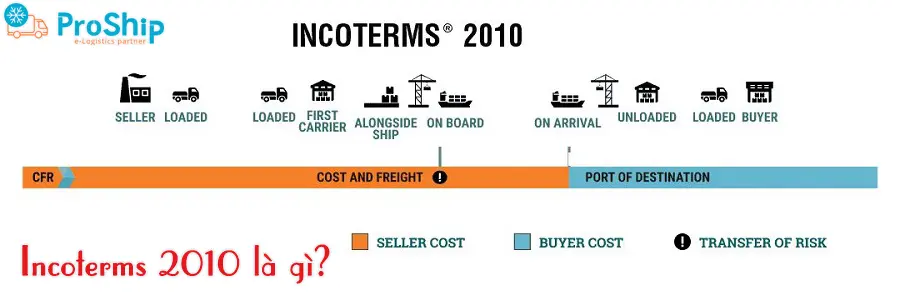
Incoterm 2010 là gì? Incoterms 2010 là bộ quy tắc được sửa đổi và soạn thảo năm 2010, gồm 11 điều khoản. Mỗi điều khoản định nghĩa cụ thể các trách nhiệm về việc giao hàng, thanh toán và bảo hiểm trong quá trình vận chuyển hàng hóa từ người bán đến người mua.
Các điều kiện quy định trong Incoterms 2010
Muốn biết Incoterm 2010 có bao nhiêu điều kiện, hãy cùng Proship cập nhật nội dung sau:
Điều kiện CIP
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid to) là cước phí bảo hiểm trả tới đích, là điều kiện Incoterm, trong đó người bán chịu trách nhiệm giao hàng đến địa điểm đã thỏa thuận tại quốc gia của người mua và phải thanh toán chi phí vận chuyển này.
Song theo nguyên tắc CIP, rủi ro của người bán sẽ kết thúc khi họ đã đặt hàng lên tàu, tại điểm xuất phát của lô hàng.
Điều kiện CIF
CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight) là tiền hàng, phí bảo hiểm và cước phí là quy định dành riêng cho vận tải biển. Theo điều kiện CIF, người bán chịu trách nhiệm về chi phí và cước phí đưa hàng đến cảng đích do người mua chỉ định.
Điều kiện CPT
CPT (Carriage Paid To) là quy định về cước phí trả tới, là nguyên tắc yêu cầu người bán phải giao hàng cho vận chuyển tại một địa điểm cụ thể. Người bán phải tự trả tiền cước phí vận chuyển để đưa hàng đến một điểm đích đã được thỏa thuận.
Người bán cũng phải chịu trách nhiệm về bảo hiểm hàng hóa trong quá trình vận chuyển đến điểm đích. Trách nhiệm người bán kết thúc khi hàng hóa đã được giao cho vận chuyển tại địa điểm thỏa thuận.
Điều kiện CFR
CFR (Cost and Freight) là tiền hàng và cước phí, nghĩa là người bán trả tiền vận chuyển hàng hóa tới cảng đích quy định. Rủi ro được chuyển giao cho người mua khi hàng hóa được xếp lên tàu tại nước xuất khẩu.
Điều kiện DAP
DAP (Delivered at Place) là quy tắc giao hàng tại nơi đến, người bán chịu trách nhiệm về mọi chi phí và rủi ro liên quan đến việc giao hàng đến địa điểm đã thỏa thuận cuối cùng.
Quy tắc DAP được sử dụng khi người mua muốn kiểm soát việc tiếp quản hàng hóa và thủ tục nhập khẩu tại điểm đến cụ thể. Trong khi đó, người bán chịu trách nhiệm giao hàng đến điểm đó.
Điều kiện DAT
DAT (Delivered At Terminal) là quy tắc giao tại bến, là bên bán giao hàng đến bến tại địa điểm mà người bán và người mua đã thỏa thuận trước đó, nó có thể là đầu mối vận tải đường bộ hoặc bến cảng.
Theo quy tắc DAT, người bán phải chịu trách nhiệm về vận chuyển hàng đến cảng đến nơi đích và phải tự trả tiền cước phí vận chuyển đến cảng này. DAT sử dụng khi người mua muốn kiểm soát việc tiếp quản hàng hóa và thủ tục nhập khẩu tại cảng đến nơi đích.
Điều kiện DDP
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) là giao tại đích đã nộp thuế, là người bán chịu trách nhiệm giao hàng đến địa điểm chỉ định tại quốc gia của người mua và thanh toán mọi chi phí đưa hàng tới điểm đến gồm thuế và thuế nhập khẩu. Trong DDP, người bán không chịu trách nhiệm dỡ hàng.
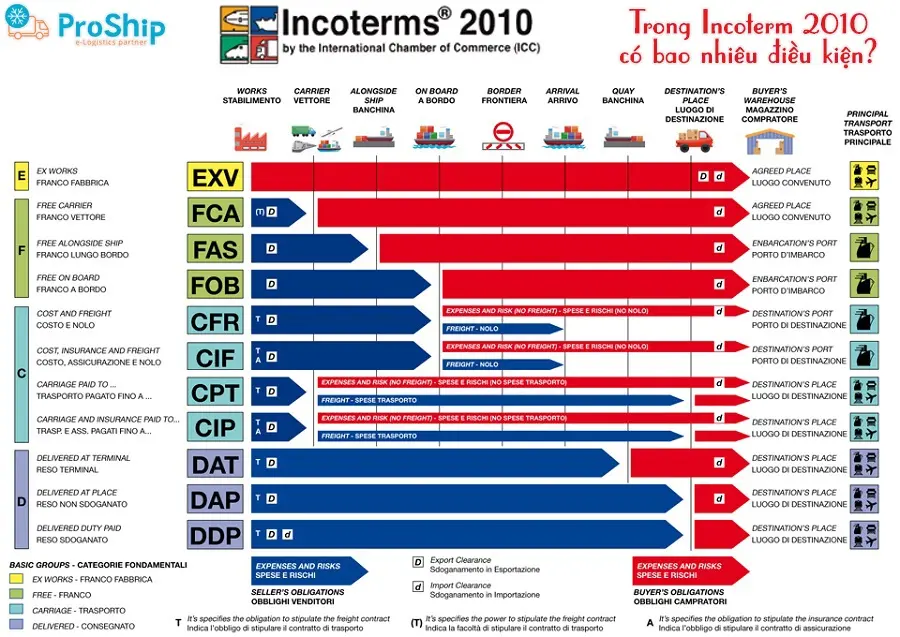
Điều kiện EXW
EXW (Ex Works) là quy tắc giao tại xưởng quy định trách nhiệm người bán là đưa hàng sẵn sàng tại xưởng của họ hoặc vị trí khác được chỉ định trước.
Trong khi đó, người mua muốn kiểm soát hoàn toàn vận chuyển và chịu trách nhiệm về mọi khía cạnh của quá trình này:
- Người mua chịu các chi phí và rủi ro từ thời điểm hàng hóa rời khỏi xưởng của người bán;
- Người mua chi trả và sắp xếp cho việc vận chuyển hàng hóa từ xưởng của người bán đến điểm đích của họ;
- Người mua phải xử lý mọi thủ tục xuất, nhập khẩu và chịu trách nhiệm về bảo hiểm và các giấy tờ liên quan.
Điều kiện FAS
FAS (Free Alongside Ship) là giao hàng dọc mạn tàu quy định người bán giao hàng khi hàng đặt dọc mạn tàu của người mua tại cảng bốc hàng đã chỉ định từ trước.
Quy tắc FAS được sử dụng khi hàng được vận chuyển bằng đường biển và người mua muốn kiểm soát việc nạp hàng lên tàu và đảm bảo rằng hàng hóa đã sẵn sàng để được nạp lên tàu tại cảng xuất phát.
Song FAS không chịu trách nhiệm về việc vận chuyển đến điểm đích của người mua. Do đó, các chi phí và trách nhiệm sau khi hàng hóa đã nằm cạnh màn tàu tại cảng xuất phát thuộc về người mua.
Điều kiện FCA
FCA (Free Carrier) là giao hàng cho người chuyên chở, là quy tắc yêu cầu người bán làm thủ tục thông quan để xuất khẩu và giao hàng cho người mua tại cơ sở của người bán hoặc giao hàng cho người mua tại địa điểm chỉ định khác.
FCA không phải là điều khoản bắt buộc trong hoạt động thương mại quốc tế. Theo đó, người bán không bắt buộc phải làm thủ tục thông quan và thanh toán thuế nhập khẩu cho lô hàng.
Điều kiện FOB
FOB (Free On Board) là giao hàng trên tàu quy định người bán chịu trách nhiệm giao hàng đã xếp lên tàu. Rủi ro được chuyển giao ngay sau khi hàng hóa được đặt xuống tàu.
Từ thời điểm hàng hóa đã được đặt trên boong tàu, người mua chịu trách nhiệm về việc tiếp quản hàng hóa, bảo hiểm hàng hóa, thủ tục hải quan xuất khẩu, cước phí vận chuyển quốc tế và mọi chi phí và rủi ro liên quan đến hàng hóa.
Incoterms 2010 đóng vai trò quan trọng ra sao?
Như trên, bạn đã có hiểu được Incoterm 2010 là gì và Incoterm 2010 có bao nhiêu điều kiện. Vậy tầm quan trọng của Incoterm 2010 thế nào, bên bán, bên mua,…bạn đã biết chưa?
Incoterms 2010 có tầm quan trọng lớn trong Thương mại quốc tế và giao dịch hàng hóa. Nó đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc xác định, rà soát các điều khoản thương mại quốc tế giữa người mua và người bán. Qua đó, giúp tối ưu hiệu suất, giảm rủi ro cho các bên liên quan.
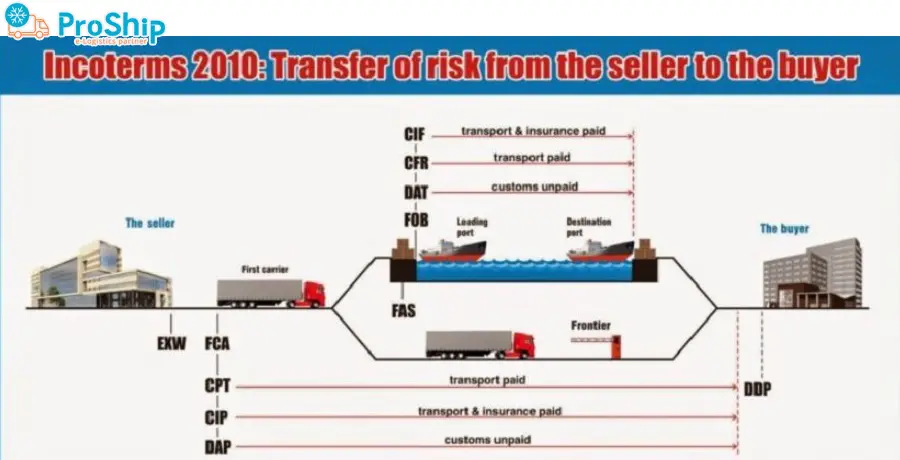
11 điều khoản quy định trong Incoterms 2010 được áp dụng cho 2 nhóm chính mà Proship ghi nhận được gồm:
- Nhóm 1: Các điều kiện, quy tắc Incoterms áp dụng cho mọi phương thức vận tải: EXW, FCA, CIP, CPT, DAT, DAP và DDP.
- Nhóm 2: Các quy tắc Incoterms áp dụng riêng cho lĩnh vực vận tải biển và đường thủy nội địa: FAS, FOB, CFR và CIF.
Trên đây là những giải đáp thắc mắc về Incoterm 2010 có bao nhiêu điều kiện, Incoterm 2010 là gì, tầm quan trọng của Incoterm 2010 ra sao. Từ đây, các cá nhân, doanh nghiệp, bên bán, bên mua,…khi tham gia vào hoạt động thương mại quốc tế và gặp vướng mắc nào có thể lưu lại, áp dụng vào các điều kiện quy định. Và khi cần sử dụng Dịch vụ vận tải Đa phương thức tại Proship, liên hệ ngay 0909 344 247.
